
In normal feet, the relationship between the talus and the 1 st metatarsal results in a straight line being formed along their axes (i.e. If the patient is unable to stand or weight-bear, a simulated weight-bearing radiograph should be obtained. The longitudinal arch of the foot must be assessed on a weight-bearing lateral foot radiograph. There is some evidence to suggest that flat feet protect against stress fractures ref. There are several conditions associated with pes planus 1,2: These deformities are usually flexible, which means that on non-weight-bearing views, the alignment of the plantar arch normalizes. Pes planus results from loss of the medial longitudinal arch and can be either rigid or flexible. Within the first decade, there is spontaneous development of a strong arch in most people 7. In the pediatric population, the degree of ligamentous laxity of the foot results in relative pes planus that resolves over time 5. posterior tibialis dysfunction (most common) 4.congenital: normal in toddlers, may persist into adulthood.Approximately 10% (range 7-15%) of the population with developmental flatfoot go on to develop symptoms requiring medical attention 7.
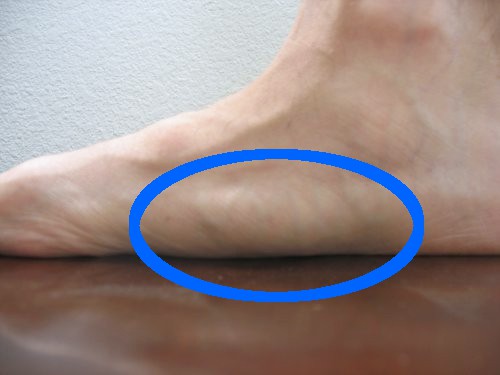
Pes planus may occur in up to 20% of the adult population, although the majority of patients are asymptomatic and require no treatment. Pes planus is also known as flatfoot, planovalgus foot or fallen arches 7.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
